
Allergic rhinitis
Allergic rhinitis is seasonal or perennial itching, sneezing, rhinorrhea, nasal congestion, and sometimes conjunctivitis, caused by exposure to pollen or other allergens.
Diagnosis is by history and skin testing .Treatment is with combination of antihistamines, decongestants, nasal corticosteroid, and for severe, refractory cases, desensitization.
Allergic rhinitis may occur seasonally (hay fever) or throughout the year (perennial rhinitis)
At least 25% of perennial rhinitis is non-allergic.
Seasonal rhinitis is caused by tree pollen e.g. (oak, elm, maple, alder, birch, juniper, olive) in spring.
Grass pollen e.g (Bermuda, timothy, sweet vernal, orchard, Johnson) and weed pollen e.g( Russian thistle, English plantain) in the summer and other weed pollen e.g ragweed in the fall.
Causes differ by region, and seasonal rhinitis is occasionally caused by airborne fungal spores.
Perennial rhinitis is caused by year-round exposure to indoor inhaled allergens (e.g. dust mite, cockroach, animal dander, and mold) or by strong reactivity to plant pollen in sequential seasons.
All allergic rhinitis and asthma frequently co-exist.
Whether rhinitis and asthma result from the same allergic process (one airway hypothesis ) or rhinitis is a discrete asthma trigger is unclear.
Nonallergic forms of perennial rhinitis include infectious, vasomotor, atrophic, hormonal, drug-induced, and gustatory rhinitis.
Symptoms and signs
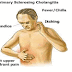
Patient have itching of the nose, eyes or mouth, sneezing, rhinorrhea and nasal and nasal and sinus obstruction.
Sinus obstruction may cause frontal headaches, sinus is a frequent complication.
Coughing and wheezing may also occur, especially if asthma is also present.
The most prominent feature of perennial rhinitis is a chronic nasal obstruction, which in children can lead to chronic otitis media.
Symptoms vary in severity throughout the year. Itching is less prominent.
Signs include edematous, bluish-red nasal turbinates, and in some cases of seasonal rhinitis, conjuntival injection and eyelid edema.
Diagnosis
Allergic rhinitis can almost always be diagnosed by history alone. Diagnostic testing is not routinely needed unless patients do not improve with empiric treatment, then skin tests showing reactions to pollens (seasonal) or to dust mite, cockroach, animal dander, mold, or other antigens (perennial) can be used to guide additional treatment.
Eosinophilia detective on nasal smear with negative skin tests suggests aspirin sensitivity or non allergic rhinitis with eosinophilia (NARES).
For infectious vasomotor, atrophic, hormonal, drug-induced, or gustatory rhinitis, diagnosis is usually by history or therapeutic trials.
Treatment
Treatment of seasonal and perennial allergic rhinitis is generally the same, although attempts at environmental control (e.g eliminating dust mites and cockroaches) are recommended for perennial rhinitis.
The most effective 1st-line drug treatments are oral antihistamines plus oral decongestants or nasal corticosteroids with or without oral antihistamines.
Less effective alternatives include nasal mast cell stabilizers (cromolyn and nedocromil) given bid to qid, the nsal H1 blocker azelastine 2 puffs once per day ,and nasal ipratropium 0.03 % 2 puffs q 4 to 6h, which relieves rhinorrhea .
Intranasal saline, often forgotten, helps mobilize thick nasalsecretions and hydrate nasal mucous membranes.
Immunotherapy may be more effective for seasonal than for allergic perennial rhinitis, it is indicated when symptoms are severe allergen cannot be avoided and drug treatment is inadequate.
First attempts at desensitization should begin soon after the pollen season ends to prepare for the next season, adverse reactions increase when desensitization is started during the pollen season because the person’s allergic immunity is already maximally stimulated.
Montelukast relieves allergic rhinitis symptoms, but its role relative to other treatments is uncertain.
Anti-lgE antibody is under study for treatment of allergic rhinitis but will probably have a limited role because less expensive, effective alternatives are available.
Treatment for NARES is nasal corticosteroids. Treatment of aspirin sensitivity is aspirin avoidance, with desensitization and leukotriene blockers as needed, nasal polyps may respond to nasal corticosteroids










0 comments :
Post a Comment