
Henoch –Schonlein Purpura
(Allergic or Anaphylactoid Purpura)
Henoch-Schonlein purpura is a vasculitis affecting primarily small vessels that occur most often in children.
Common manifestation include palpable purpura,arthralgias, GI symptoms and signs, and glomerulonephritis.
Diagnosis is clinical. Disease is usually self limited.
Corticosteroids can relieve arthralgias and GI symptoms but do not alter the course of disease.
Progressive glomerulonephritis may require high dose corticosteroids and cyclophosphamide.
Henoch-Schonlein purpura (HSP) is caused by deposition of lgA-containing immune complexes in small arteries of skin and other sites, with consequent activation of complement.
Possible inciting antigens include URI viruses, drugs, foods, insect bites and immunizations.
The typical renal lesion is focal,segmental proliferative glomerulonephritis.
Symptoms and Signs
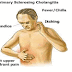
The disease begins with a sudden palpable purpuric rash that typically involves the extensor surfaces of the feet ,legs and arms and a strip across the buttock.
The purpura may start as small areas of urticaria that become indurated and palpable.Crops of new lesions may appear over days to several weeks .
Many patients also have fever and polyarthralgia with associated periarticular tenderness and swelling of the ankles ,knees,hips,wrists and elbows.
GI manifestations are common and include colicky abdominal pain, abdominal tenderness, and melena.
Intussusception occasionally develops. Stool may test positive for occult blood .
Symptoms usually remit after about 4 wk but often recur at least once after a disease-free interval of several weeks.
In most patients, the disorder subsides without serious sequelae,however some patients develop chronic renal failure.
Diagnosis,Prognosis and Treatment.
HSP should be suspected in patients particularly children,with typical skin findings
The clinical diagnosis is confirmed by biopsy of skin lesion, with identification of leukocytoclastic vasculitis with lgA in the vessel walls.
Hematuria,proteinuria, and RBC casts indicate kidney involvement .Renal biopsy should be obtained if renal function is deteriorating and may help define the prognosis.
Diffuse glomerular involvement or crescentic changes in most glomeruli predict progressive renal failure.
Treatment except for the elimination of a possible offending drug is primarily symptomatic.
Corticosteroids (e.g prednisone 2 mg/kg up to a total of 50mg po once per day) may help to control edema,joint pain,and abdominal pain but their effect on renal involvement is unclear . Nevertheless immunosuppressive therapy (pulse IV methylprednidolone followed by oral prednisone and cyclophosphamide) can be given t attempt to control inflammation in patients who develop severe renal disease.
Henoch-Schonlein purpura is a vasculitis affecting primarily small vessels that occur most often in children.
Common manifestation include palpable purpura,arthralgias, GI symptoms and signs, and glomerulonephritis.
Diagnosis is clinical. Disease is usually self limited.
Corticosteroids can relieve arthralgias and GI symptoms but do not alter the course of disease.
Progressive glomerulonephritis may require high dose corticosteroids and cyclophosphamide.
Henoch-Schonlein purpura (HSP) is caused by deposition of lgA-containing immune complexes in small arteries of skin and other sites, with consequent activation of complement.
Possible inciting antigens include URI viruses, drugs, foods, insect bites and immunizations.
The typical renal lesion is focal,segmental proliferative glomerulonephritis.
Symptoms and Signs
The disease begins with a sudden palpable purpuric rash that typically involves the extensor surfaces of the feet ,legs and arms and a strip across the buttock.
The purpura may start as small areas of urticaria that become indurated and palpable.Crops of new lesions may appear over days to several weeks .
Many patients also have fever and polyarthralgia with associated periarticular tenderness and swelling of the ankles ,knees,hips,wrists and elbows.
GI manifestations are common and include colicky abdominal pain, abdominal tenderness, and melena.
Intussusception occasionally develops. Stool may test positive for occult blood .
Symptoms usually remit after about 4 wk but often recur at least once after a disease-free interval of several weeks.
In most patients, the disorder subsides without serious sequelae,however some patients develop chronic renal failure.
Diagnosis,Prognosis and Treatment.
HSP should be suspected in patients particularly children,with typical skin findings
The clinical diagnosis is confirmed by biopsy of skin lesion, with identification of leukocytoclastic vasculitis with lgA in the vessel walls.
Hematuria,proteinuria, and RBC casts indicate kidney involvement .Renal biopsy should be obtained if renal function is deteriorating and may help define the prognosis.
Diffuse glomerular involvement or crescentic changes in most glomeruli predict progressive renal failure.
Treatment except for the elimination of a possible offending drug is primarily symptomatic.
Corticosteroids (e.g prednisone 2 mg/kg up to a total of 50mg po once per day) may help to control edema,joint pain,and abdominal pain but their effect on renal involvement is unclear . Nevertheless immunosuppressive therapy (pulse IV methylprednidolone followed by oral prednisone and cyclophosphamide) can be given t attempt to control inflammation in patients who develop severe renal disease.










0 comments :
Post a Comment